Please help me . i need the procedure of MIC method of analysis
What is abbreviation of MIC
Minimum inhibitions Consantaraton
For what product ?
as antiseptic API povidone Iodine
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) / Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
‘Minimum inhibitory concentration’ (MIC) is defined as the ‘lowest concentration’ of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a specified micro-organism after overnight incubation, and ‘Minimum bactericidal concentrations’ (MBCs) as the ‘lowest concentration’ of antimicrobial that will prevent the growth of a specified micro-organism.
MODEL UTILITY:
This “in vitro” antimicrobial assay is typically used as an initial screening to determine possible antimicrobial activity of novel materials. This assay determines the lowest concentration of the novel material that still shows antimicrobial activity.
HOW THE MODEL WORKS:
In this assay, the test material is serially diluted, typically a doubling dilution, in a growth medium. Then an aliquot of prepared bacterial solution is added to each dilution in the series. The dilutions are then incubated overnight, and then observed for turbidity. The dilution with the lowest concentration of the test material that exhibits no turbidity is determined to be the minimum inhibition concentration (MIC).
An aliquot is taken from each dilution in the series that exhibited no growth and is further diluted, typically a hundred-fold dilution, in fresh growth medium. These new hundred-fold dilutions are then incubated overnight and observed for turbidity. The lowest concentration of the test material in the first dilution series that correlated with the hundred-fold dilution that exhibits no turbidity is determined to be the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC).
This data is from a study comparing several formulations of a novel surgical rinse to a predicate device, povidone iodine. The test organism for this study was “Staphylococcus aureus”.
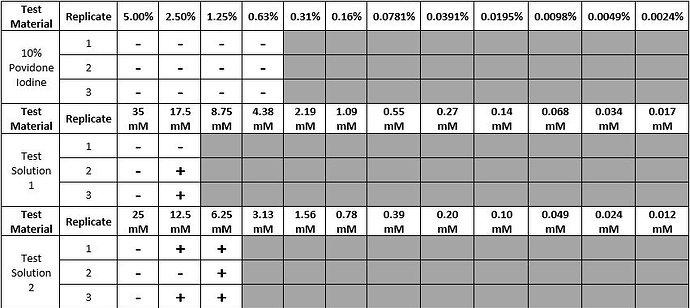
Table 1. This table compares the results of the minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) testing for povidone iodine and two test materials. This table indicates no turbidity with a “-” and turbidity with a “+”. The minimum inhibition concentration for povidone iodine was determined to be 0.63% povidone iodine. The minimum inhibition concentration for Test Solution 1 and Test Solution 2 were determined be 17.5 mM and 6.25 mM, respectively.
Table 2. This table compares the results of the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) testing for povidone iodine and two test materials. This table indicates no turbidity with a “-” and turbidity with a “+”. The minimum bactericidal concentration for povidone iodine was determined to be 0.63% povidone iodine. The minimum bactericidal concentration for Test Solution 1 and Test Solution 2 were determined be 35 mM and 25 mM, respectively.
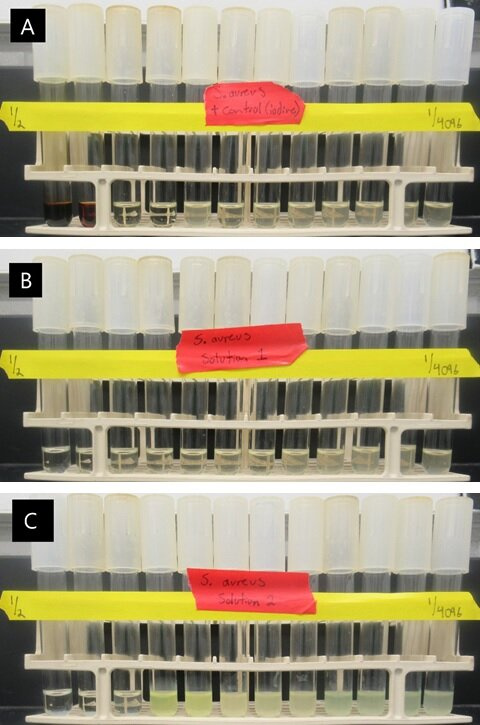

Figure 1. Example photographs of minimum inhibition concentration serial dilutions. The dilution factor is indicated on the yellow bar. (A) Serial dilution of povidone iodine with the turbidity beginning at the 5th dilution. (B) Serial dilution of Test Solution 1 with the turbidity beginning at the 3rd dilution. (C) Serial dilution of Test Solution 2 with the turbidity beginning at the 4th dilution.
ADVANTAGES:
This model is inexpensive and allows for high throughput screening of novel materials. This model also provides insight into potential starting points for the concentration of the novel materials in formulations to be used for in vivo testing.
DISADVANTAGES:
This “in vitro” model does not consistently predict anti-microbial activity when the material is used in an “in vivo” model, as is common with many “in vitro” tests.
[Reference:- Bridgepts.com]
BRIDGE PTS (Preclinical Testing Services) was founded in 2006 to meet the growing need for contract testing services in the areas of wound healing and biofilm-related infections.
The testing lab objective is to provide high quality testing services with a rapid turnaround time to help customers identify and validate their drugs and medical devices.
Additionally, the lab is committed to continual innovation in the development of novel “in vivo” testing systems and models that closely approximate their human disease counterparts. Their research into new model development represents their commitment to customers to provide the most advanced tools available in support of preclinical efficacy testing.